Wharowharo ki ngā pakeke Colds in adults
Symptoms of a cold
If you have a cold, you will have some or all of these symptoms:
- runny or blocked nose
- watery eyes
- sneezing
- itchy or sore throat
- cough, often producing mucus (sputum or phlegm) and more annoying during the night and when you wake
- hoarse voice.
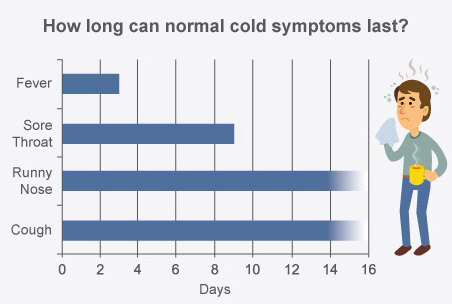
Symptoms tend to peak after 2 to 3 days but the cough that comes with a cold can last for 3 to 4 weeks.
While your immune system is fighting the cold, any mucus you are coughing up may go from white or clear to yellow or pale green. This is normal. As long as it is just a small amount and you do not have any other chest symptoms, you do not need antibiotics.
You should see your healthcare provider if you:
- have a rash (spots on your skin)
- are short of breath (feel puffed), are breathing noisily or are coughing up a lot of green or blood-stained mucus
- have dry coughing fits that make it hard to breathe
- cannot keep food or drink down and do not pass much wee (urine)
- have pain anywhere that is getting worse, despite taking paracetamol
- have had a wet-sounding cough for 4 weeks or have had the cold for 4 weeks and you are not getting better.
Avoid getting colds
Unlike flu, there is no vaccine for colds because they are caused by many different viruses.
You can avoid colds by:
- washing your hands before eating or preparing food
- not sharing cups, drink bottles, knives and forks, or anything you eat or drink with
- washing your hands after you have touched your face.
How to clean your hands [PDF, 404 KB]internal link
Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your arm (but not your hand) when you sneeze or cough, then wash your hands afterwards.
Keeping your home warm and dry and being smokefree also help to stop you and your family from getting colds.
Getting enough sleep and eating well can also reduce the number of colds you get and how bad they are.
Clinical review
This content was written by HealthInfo clinical advisers. It has been adapted for Health Information and Services.